Little Endian:
Little Endian means that the lower order byte of the number is stored in memory at the lowest address, and the higher order byte is stored at the highest address.
Big Endian:
Big Endian means that the higher order byte of the number is stored in memory at the lowest address, and the lower order byte is stored at the highest address.
//C program to convert little Endian to Big Endian//
#include <stdio.h>
int changed_endian(int num)
{
int byte0, byte1, byte2, byte3;
byte0 = (num & 0x000000FF) >> 0 ;
byte1 = (num & 0x0000FF00) >> 8 ;
byte2 = (num & 0x00FF0000) >> 16 ;
byte3 = (num & 0xFF000000) >> 24 ;
return((byte0 << 24) | (byte1 << 16) | (byte2 << 8) | (byte3 << 0));
}
int main()
{
int number=10;
int new_number;
new_number=changed_endian(number);
printf("New number is %d", new_number);
return 0;
}
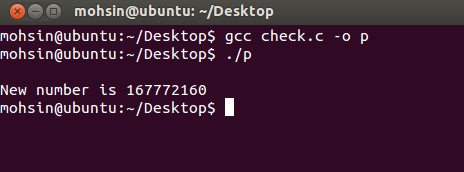
Output of the above Program:
See also:
Check system is Big Endian or Little Endiane
Little Endian means that the lower order byte of the number is stored in memory at the lowest address, and the higher order byte is stored at the highest address.
Big Endian:
Big Endian means that the higher order byte of the number is stored in memory at the lowest address, and the lower order byte is stored at the highest address.
//C program to convert little Endian to Big Endian//
#include <stdio.h>
int changed_endian(int num)
{
int byte0, byte1, byte2, byte3;
byte0 = (num & 0x000000FF) >> 0 ;
byte1 = (num & 0x0000FF00) >> 8 ;
byte2 = (num & 0x00FF0000) >> 16 ;
byte3 = (num & 0xFF000000) >> 24 ;
return((byte0 << 24) | (byte1 << 16) | (byte2 << 8) | (byte3 << 0));
}
int main()
{
int number=10;
int new_number;
new_number=changed_endian(number);
printf("New number is %d", new_number);
return 0;
}
Output of the above Program:
 |
| Convert Little Endian to Big Endian |
See also:
Check system is Big Endian or Little Endiane






No comments:
Post a Comment